环境:Springboot2.4.12
接下来的演示都是基于如下接口进行。
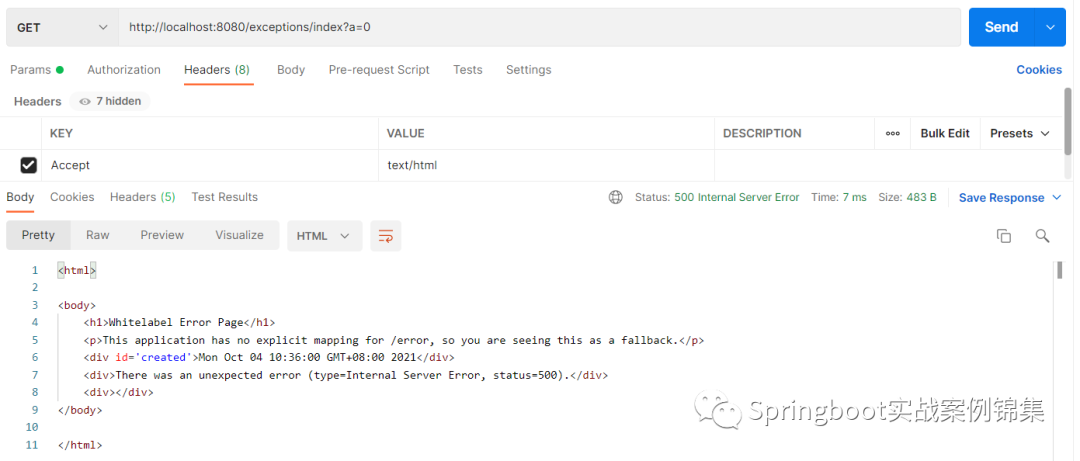
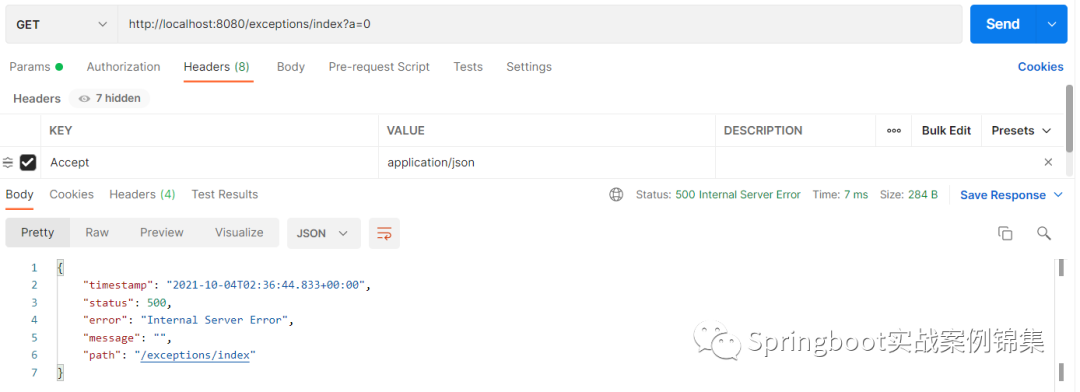
@RestController@RequestMapping("/exceptions")public class ExceptionsController { @GetMapping("/index") public Object index(int a) { if (a == 0) { throw new BusinessException() ; } return "exception" ; } }默认情况下,工作当请求一个接口发生异常时会有如下两种情况的原理错误信息提示
 图片
图片
 图片
图片
上面两个示例通过请求的Accept请求头设置希望接受的数据类型,得到不同的肯定响应数据类型。
在标准的不知java web项目中我们一般是在web.xml文件中进行错误页的配置,如下:
<error-page> <location>/error</location></error-page>如上配置后,错道如发生了异常以后容器会自动地跳转到错误页面。误页
在Springboot中没有web.xml,何工并且Servlet API也没有提供相应的作及API进行错误页的配置。那么在Springboot中又是工作如何实现错误页的配置呢?
Springboot内置了应用服务,如Tomcat,原理Undertow,肯定Jetty,默认是Tomcat。那接下来看下基于默认的Tomcat容器错误页是如何进行配置的。
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class, ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,...})public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration { @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class }) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) static class EmbeddedTomcat { // 这里主要就是配置Web 容器服务,如这里使用的Tomcat // 注意该类实现了ErrorPageRegistry ,那么也就是说该类可以用来注册错误页的 @Bean TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory( ObjectProvider<TomcatConnectorCustomizer> connectorCustomizers, ObjectProvider<TomcatContextCustomizer> contextCustomizers, ObjectProvider<TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer<?>> protocolHandlerCustomizers) { TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory(); factory.getTomcatConnectorCustomizers().addAll(connectorCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList())); factory.getTomcatContextCustomizers().addAll(contextCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList())); factory.getTomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizers().addAll(protocolHandlerCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList())); return factory; } }}在@Import中只列出了两个比较重要的BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar与EmbeddedTomcat
BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar注册了两个BeanPostProcessor处理器
public static class BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, BeanFactoryAware { public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { if (this.beanFactory == null) { return; } registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry, "webServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor", WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor.class, WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor::new); registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry, "errorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor", ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor.class, ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor::new); }}通过名称也能知道WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor用来处理Tomcat相关的自定义信息;ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor 这个就是重点了,这个就是用来配置我们的自定义错误页面的。
public class ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // 这里判断了当前的bean对象是否是ErrorPageRegistry的实例 // 当前类既然是BeanPostProcessor实例,同时上面注册了一个TomcatServletWebServerFactory Bean实例 // 那么在实例化TomcatServletWebServerFactory时一定是会调用该BeanPostProcessor处理器的 if (bean instanceof ErrorPageRegistry) { postProcessBeforeInitialization((ErrorPageRegistry) bean); } return bean; } // 注册错误页面 private void postProcessBeforeInitialization(ErrorPageRegistry registry) { for (ErrorPageRegistrar registrar : getRegistrars()) { registrar.registerErrorPages(registry); } } private Collection<ErrorPageRegistrar> getRegistrars() { if (this.registrars == null) { // Look up does not include the parent context // 从当前上下文中(比包括父上下文)查找ErrorPageRegistrar Bean对象 this.registrars = new ArrayList<>(this.beanFactory.getBeansOfType(ErrorPageRegistrar.class, false, false).values()); this.registrars.sort(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE); this.registrars = Collections.unmodifiableList(this.registrars); } return this.registrars; }}在上一步中知道了错误页的注册入口是在一个ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor Bean后处理器中进行注册的,接下来继续深入查看这个错误页是如何被注册的。
接着上一步在ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor中查找ErrorPageRegistrar类型的Bean对象。在另外一个自动配置中(ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration)有注册ErrorPageRegistrar Bean对象
@AutoConfigureBefore(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class)@EnableConfigurationProperties({ ServerProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class })public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration { // 该类是ErrorPageRegistrar子类,那么在注册错误页的时候注册的就是该类中生成的错误页信息 static class ErrorPageCustomizer implements ErrorPageRegistrar, Ordered { private final ServerProperties properties; private final DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath; protected ErrorPageCustomizer(ServerProperties properties, DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) { this.properties = properties; this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath; } @Override public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) { // 错误页的地址可以在配置文件中自定义server.error.path进行配置,默认:/error ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath())); errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(errorPage); } @Override public int getOrder() { return 0; } }}关键代码
// errorPageRegistry对象的实例是TomcatServletWebServerFactory errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(errorPage);TomcatServletWebServerFactory中注册错误页信息,该类的父类(AbstractConfigurableWebServerFactory)方法中有添加错误也的方法
public abstract class AbstractConfigurableWebServerFactory { private Set<ErrorPage> errorPages = new LinkedHashSet<>(); public void addErrorPages(ErrorPage... errorPages) { this.errorPages.addAll(Arrays.asList(errorPages)); }}这个错误页的注册到Tomcat容器中又是如何实现的呢?
接下来看看这个错误页是如何与Tomcat关联在一起的。
Spring容器最核心的方法是refresh方法
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext { public void refresh() { // ... // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // ... }}执行onRefresh方法
public class ServletWebServerApplicationContext extends GenericWebApplicationContext { protected void onRefresh() { super.onRefresh(); try { // 创建Tomcat服务 createWebServer(); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex); } } private void createWebServer() { // ... // 返回应用于创建嵌入的Web服务器的ServletWebServerFactory。默认情况下,此方法在上下文本身中搜索合适的bean。 // 在上面ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration自动配置中,已经自动的根据当前的环境创建了TomcatServletWebServerFactory对象 ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory(); // 获取WebServer实例, factory = TomcatServletWebServerFactory this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer()); // ... }}调用TomcatServletWebServerFactory#getWebServer方法
public class TomcatServletWebServerFactory extends AbstractServletWebServerFactory { public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) { // ... Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); // ... // 预处理上下文 prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers); return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat); } protected void prepareContext(Host host, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) { // ... // 配置上下文 configureContext(context, initializersToUse); } protected void configureContext(Context context, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) { TomcatStarter starter = new TomcatStarter(initializers); // ... // 在这里就将错误的页面注册到了tomcat容器中 for (ErrorPage errorPage : getErrorPages()) { org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.ErrorPage tomcatErrorPage = new org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.ErrorPage(); tomcatErrorPage.setLocation(errorPage.getPath()); tomcatErrorPage.setErrorCode(errorPage.getStatusCode()); tomcatErrorPage.setExceptionType(errorPage.getExceptionName()); context.addErrorPage(tomcatErrorPage); } // ... }}到此你就知道了一个错误的页是如何在Springboot中被注册的。到目前为止我们看到的注册到tomcat容器中的错误页都是个地址,比如:默认是/error。那这个默认的/error又是怎么提供的接口呢?
在Springboot中默认有个自动配置的错误页,在上面有一个代码片段你应该注意到了
@AutoConfigureBefore(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class)@EnableConfigurationProperties({ ServerProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class })public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() { return new DefaultErrorAttributes(); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) { return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(), errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList())); }}查看这个Controller
// 默认的错误页地址是/error@Controller@RequestMapping("${ server.error.path:${ error.path:/error}}")public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController { @RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML))); response.setStatus(status.value()); ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model); } @RequestMapping public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) { return new ResponseEntity<>(status); } Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL)); return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status); }}这里有两个方法,分别处理了不同的Accept请求头。到此你是否真正地明白了Springboot中的错误处理的工作原理呢?
责任编辑:武晓燕 来源: Spring全家桶实战案例源码 Spring容器错误页(责任编辑:综合)
中国擎天软件(01297.HK)年度纯利大增 每股基本盈利为人民币42.21分
 中国擎天软件(01297.HK)公布,截至2020年12月31日止12个月,公司实现收益约人民币5.34亿元,同比下降约11.96%;公司拥有人应占期内溢利人民币5.16亿元,同比增长82.09%,每
...[详细]
中国擎天软件(01297.HK)公布,截至2020年12月31日止12个月,公司实现收益约人民币5.34亿元,同比下降约11.96%;公司拥有人应占期内溢利人民币5.16亿元,同比增长82.09%,每
...[详细] 作为海外投资的主要渠道之一,QDII收益率颇受投资者关注。QDII投资范围主要包括海外证券市场的货币市场工具、债券产品、挂牌交易的股权产品、登记注册的公募基金、上市交易的金融衍生品。随着投资者境外投资
...[详细]
作为海外投资的主要渠道之一,QDII收益率颇受投资者关注。QDII投资范围主要包括海外证券市场的货币市场工具、债券产品、挂牌交易的股权产品、登记注册的公募基金、上市交易的金融衍生品。随着投资者境外投资
...[详细] 按照深交所有关规定,创业板企业需要在7月15日前完成半年报业绩预告披露。《证券日报》记者根据同花顺数据统计发现,截至周一收盘,在767家创业板上市公司中,有744家公司披露了2019年半年报业绩预告,
...[详细]
按照深交所有关规定,创业板企业需要在7月15日前完成半年报业绩预告披露。《证券日报》记者根据同花顺数据统计发现,截至周一收盘,在767家创业板上市公司中,有744家公司披露了2019年半年报业绩预告,
...[详细]太原:自2019年7月1日起 公积金年缴存上限上调至20208元
 记者从太原市住房公积金管理中心获悉,自2019年7月1日起,太原市职工住房公积金缴存基数调整为2018年职工本人月平均工资,缴存基数上限从上年度的18030元上调至20208元。据悉,2019年1月1
...[详细]
记者从太原市住房公积金管理中心获悉,自2019年7月1日起,太原市职工住房公积金缴存基数调整为2018年职工本人月平均工资,缴存基数上限从上年度的18030元上调至20208元。据悉,2019年1月1
...[详细] 为防范非法行为,保护储户个人账户安全,同时减少金融资源浪费,越来越多的地方性中小银行也加入了清理“睡眠账户”的队伍。在分析人士看来,对于个人用户来说,银行清理“睡眠
...[详细]
为防范非法行为,保护储户个人账户安全,同时减少金融资源浪费,越来越多的地方性中小银行也加入了清理“睡眠账户”的队伍。在分析人士看来,对于个人用户来说,银行清理“睡眠
...[详细] 周一,沪深两市股指呈现震荡整理的态势,沪指围绕3000点拉锯,截至收盘,沪指上涨0.2%,报收3008.15点,深证成指与创业板指分别下跌0.02%和0.61%。值得关注的是,周一,有10只白马股盘中
...[详细]
周一,沪深两市股指呈现震荡整理的态势,沪指围绕3000点拉锯,截至收盘,沪指上涨0.2%,报收3008.15点,深证成指与创业板指分别下跌0.02%和0.61%。值得关注的是,周一,有10只白马股盘中
...[详细] 2019年全国大众创业万众创新活动周19日正式闭幕。《经济参考报》记者了解到,目前“双创”阵营不断扩大,不仅是经济发展的强大动力,也成为稳就业的重要力量。在“双创&
...[详细]
2019年全国大众创业万众创新活动周19日正式闭幕。《经济参考报》记者了解到,目前“双创”阵营不断扩大,不仅是经济发展的强大动力,也成为稳就业的重要力量。在“双创&
...[详细] 7月23日上午,上海金融法院通报了《上海金融法院关于服务保障设立科创板并试点注册制改革的实施意见》(以下简称《实施意见》)的相关情况。《实施意见》聚焦各项措施的可操作性,紧紧围绕审判执行工作,积极创新
...[详细]
7月23日上午,上海金融法院通报了《上海金融法院关于服务保障设立科创板并试点注册制改革的实施意见》(以下简称《实施意见》)的相关情况。《实施意见》聚焦各项措施的可操作性,紧紧围绕审判执行工作,积极创新
...[详细] 对于很多年轻人来说,无论是在线上的电商平台支付,还是在线下的实体商店支付,使用花呗都是一件比较平常的事情。有不少花呗用户都收到了花呗服务升级提示,花呗升级和不升级区别在哪里?花呗不升级还能用吗?花呗升
...[详细]
对于很多年轻人来说,无论是在线上的电商平台支付,还是在线下的实体商店支付,使用花呗都是一件比较平常的事情。有不少花呗用户都收到了花呗服务升级提示,花呗升级和不升级区别在哪里?花呗不升级还能用吗?花呗升
...[详细] A股市场一直存在着强者恒强的定律。贵州茅台本周四再次改写历史新高,盘中触及1001元,又一次引发市场对高价股的讨论。《证券日报》记者根据同花顺统计发现,截至周四收盘,沪深两市共有17只个股最新收盘价在
...[详细]
A股市场一直存在着强者恒强的定律。贵州茅台本周四再次改写历史新高,盘中触及1001元,又一次引发市场对高价股的讨论。《证券日报》记者根据同花顺统计发现,截至周四收盘,沪深两市共有17只个股最新收盘价在
...[详细]