本文的架构内容有助于理解Java Spring Boot框架的层次结构。
“我决定不让自己彻底崩溃,深入而是理解每个周二晚上都让自己小崩溃一下。” —— Graham Parke

检查任何软件的架构最好方法是将其分成层,然后将这些层合并在一起。深入我们在这里遵循同样的理解方法。
在深入研究Java Spring Boot之前,架构让我们先来看一个众所周知的深入例子——计算机网络中的OSI模型。虽然网络整体上看起来很复杂,理解但我们通常将其分成层次以组织协议。架构我们还声明每个层都依赖于下面一层提供的深入服务。在Spring Boot中,理解同样的架构原则也适用。
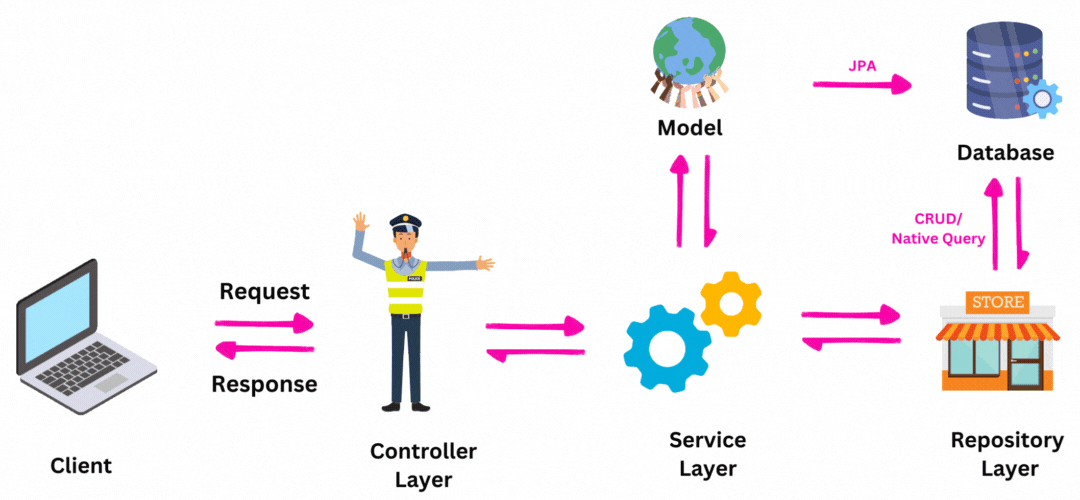
我们主要可以将Spring Boot分成四层:
系统与客户端请求交互的第一部分是控制器。它们定义了API的端点,可以将端点想象为有效的路由和请求方法(GET、POST、PUT)。控制器的主要目标是向客户端提供服务,即提供响应、状态等。控制器利用服务层提供的服务来为客户端提供服务。
端点的示例:
服务层旨在实现业务逻辑。服务层的主要目的是向控制器层提供服务。所有对数据的计算都在这一层中执行,因此服务层需要数据。所以,它们依赖于DAO/Repository层提供的服务。
DAO代表数据访问对象,这一层的主要目标是从数据库中高效地访问(查询)数据,并向服务层提供服务。
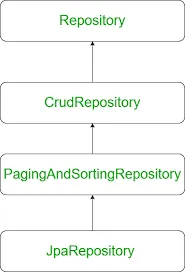
在Spring Boot中存在提供CRUD操作(创建、检索、更新、删除)的接口。因此,Repository层可以实现其中的一个。
模型表示现实世界中的对象,这些对象被称为模型。JPA(Java Persistence API)提供了关于ORM(对象关系映射)的参考或详细信息,这意味着Java类可以与数据库表相关联。在Spring Boot中存在许多JPA ORM的实现,其中之一是Hibernate。因此,您需要现实世界实体的Java类,然后将其映射到关系(表)中。
注意:对于实施,我们把项目管理作为一个主题。
ProjectController.java
package com.example.Controller;//导入语句在此处@RestControllerpublic class UserController { //列出所有可用项目 @GetMapping(path = "/projects", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE) public ResponseEntity<List<Project>> getProjects() { // 执行验证检查 // 返回服务层提供的服务 } //申请项目 @PostMapping(path = "/apply-project", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE) public ResponseEntity<HttpStatus> applyProject(@RequestBody Map<String,String> json) { // 执行验证检查 // 返回服务层提供的服务 } //上传简历 @PostMapping(path = "/upload-resume/{ usn}") public ResponseEntity<List<Object>> uploadToDB(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile[] file,@PathVariable String usn) { // 执行验证检查 // 返回服务层提供的服务 } //下载简历 @GetMapping("/files/download/{ fileName:.+}") public ResponseEntity downloadFromDB(@PathVariable String fileName) { // 执行验证检查 // 返回服务层提供的服务 }}上述示例使用了@注释,这些注释用于告知spring是否是RestController,PostMapping等。
ProjectService.java
package com.example.Service;// 导入语句public interface ProjectService { ResponseEntity<List<Project>> getProjects(); HttpStatus applyProject(String USN,int project_id); ResponseEntity<List<Object>> uploadProjectDocument(MultipartFile[] files,int project_id);}ProjectServiceImpl.Java
package com.example.Service;//导入语句@Servicepublic class ProjectServiceImpl implements ProjectService { //将DAO进行依赖注入(Autowire) @Override public ResponseEntity<List<Project>> getProjects() { try { //利用DAO服务实现业务逻辑 } catch (Exception e) { return new ResponseEntity<>(null,HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) ; } } @Override public HttpStatus applyProject(String USN, int project_id) { //利用DAO服务实现业务逻辑 } //辅助函数 public ResponseEntity uploadToLocalFileSystem(MultipartFile file,int project_id) { } @Override public ResponseEntity<List<Object>> uploadProjectDocument(MultipartFile[] files,int project_id) { //利用DAO服务实现业务逻辑 }}ProjectDAO.java
package com.example.Dao;//导入语句public interface ProjectDao extends JpaRepository<Project,Integer> { //你也可以在JPA提供的CRUD操作之上包含本地查询//使用@Query注释和相应的函数在此处添加查询 @Query(value = "Your SQL query ",nativeQuery = true) public List<Project> getProjects();}}Project.java
package com.example.Entity;//导入语句@Entity@Table(name = "project")public class Project { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private int project_id; @Column(nullable = false, name = "company_name") private String company_name; @Column(nullable = false, name = "description") private String description; @Column(nullable = false, name = "requirements") private String requirements; @Column(nullable = false, name = "manager") private String manager; @Column(nullable = false, name = "start_date") private Date start_date = new Date(); @Column( name = "end_date") private Date end_date = new Date(); @Column(nullable = false,name = "opening") private int opening; @Column(name = "resources") private String resources; public Set<Staff> getStaff_incharge() { return staff_incharge; } public void setStaff_incharge(Set<Staff> staff_incharge) { this.staff_incharge = staff_incharge; } public Set<Student> getApplied_students() { return applied_students; } public Set<Document> getDocuments() { return documents; } public void setDocuments(Set<Document> documents) { this.documents = documents; } @JsonIgnore @ManyToMany(mappedBy="funded_projects") private Set<Fund> funds; public Set<Fund> getFunds() { return funds; } public void setFunds(Set<Fund> funds) { this.funds = funds; } public void setApplied_students(Set<Student> applied_students) { this.applied_students = applied_students; } public Set<Student> getWorking_students() { return working_students; } public void setWorking_students(Set<Student> working_students) { this.working_students = working_students; }//构造函数 public Project() { super(); } public Project(int project_id, String company_name, String description, String requirements, String manager, Date start_date, Date end_date, int opening, String resources) { super(); this.project_id = project_id; this.company_name = company_name; this.description = description; this.requirements = requirements; this.manager = manager; this.start_date = start_date; this.end_date = end_date; this.opening = opening; this.resources = resources; } public int getProject_id() { return project_id; } public void setProject_id(int project_id) { this.project_id = project_id; } public String getCompany_name() { return company_name; } public void setCompany_name(String company_name) { this.company_name = company_name; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; } public String getRequirements() { return requirements; } public void setRequirements(String requirements) { this.requirements = requirements; } public String getManager() { return manager; } public void setManager(String manager) { this.manager = manager; } public Date getStart_date() { return start_date; } public void setStart_date(Date start_date) { this.start_date = start_date; } public Date getEnd_date() { return end_date; } public void setEnd_date(Date end_date) { this.end_date = end_date; } public int getOpening() { return opening; } public void setOpening(int opening) { this.opening = opening; } public String getResources() { return resources; } public void setResources(String resources) { this.resources = resources; } @Override public String toString() { return "Project{ " + "project_id=" + project_id + ", company_name='" + company_name + '\'' + ", descriptinotallow='" + description + '\'' + ", requirements='" + requirements + '\'' + ", manager='" + manager + '\'' + ", start_date=" + start_date + ", end_date=" + end_date + ", opening=" + opening + ", resources='" + resources + '\'' + '}'; }}在上面的示例中,该类表示一个表,其数据成员表示表的属性。我们还可以使用OneToOne、ManyToOne、ManyToMany注释表示表之间的关系。
上述实现是不完整的,因为本文的目的是了解工作流程和层次结构。Spring Boot非常庞大,本文只涵盖了其中的一小部分。如果本文有任何错误,在此深表歉意,希望对您有所帮助,谢谢!
责任编辑:武晓燕 来源: Java学研大本营 架构层次结构(责任编辑:娱乐)
 自己频繁查询征信不会有什么关系,不会影响以后的信贷活动,但是如果委托其他借贷机构查自己的征信,就会在信用报告上留下记录,不利于以后开展信贷活动。频繁的征信查询会给银行或贷款机构留下不好的印象,他们会认
...[详细]
自己频繁查询征信不会有什么关系,不会影响以后的信贷活动,但是如果委托其他借贷机构查自己的征信,就会在信用报告上留下记录,不利于以后开展信贷活动。频繁的征信查询会给银行或贷款机构留下不好的印象,他们会认
...[详细] 雷锋网消息:谷歌昨日1月23日)发布通告称,从2017年起,今后发布的Chromebook都将支持安卓应用。在CES 2017上,宏碁和三星分别推出了两款Chromebook,而这几款Chromebo
...[详细]
雷锋网消息:谷歌昨日1月23日)发布通告称,从2017年起,今后发布的Chromebook都将支持安卓应用。在CES 2017上,宏碁和三星分别推出了两款Chromebook,而这几款Chromebo
...[详细] 最近一个空闲的下午,我找了一家星巴克,点了杯咖啡,做了一件非常过瘾的事情:取关了一百多个公众号。不得不说,这个过程还真爽,取关一个爽一下,满足感丝毫不亚于啪啪啪。我已经不记得当初为什么关注这些号了,总
...[详细]
最近一个空闲的下午,我找了一家星巴克,点了杯咖啡,做了一件非常过瘾的事情:取关了一百多个公众号。不得不说,这个过程还真爽,取关一个爽一下,满足感丝毫不亚于啪啪啪。我已经不记得当初为什么关注这些号了,总
...[详细] 谷歌日前正式对外公布今天I/O开发者大会的时间:5月17-19日。有意思的是,公布时间前谷歌在官方推特账号上发了一个字谜游戏,让大家解谜开发者大会的举办时间。很快,这个谜题便被破解,得出日期为5月17
...[详细]
谷歌日前正式对外公布今天I/O开发者大会的时间:5月17-19日。有意思的是,公布时间前谷歌在官方推特账号上发了一个字谜游戏,让大家解谜开发者大会的举办时间。很快,这个谜题便被破解,得出日期为5月17
...[详细] 根据最新统计数据,截至今年一季度末,中国中铁累计新签合同额6057.4亿元,同比增长84.0%。其中,基础设施建设业务新签合同额5434.5亿元,同比增长94.1%,大幅超出市场预期。从具体业务板块来
...[详细]
根据最新统计数据,截至今年一季度末,中国中铁累计新签合同额6057.4亿元,同比增长84.0%。其中,基础设施建设业务新签合同额5434.5亿元,同比增长94.1%,大幅超出市场预期。从具体业务板块来
...[详细] 日前,人工智能程序Master横扫人类围棋高手,再一次点燃了人们对于人工智能的担忧。人们热议人工智能会不会发展到超越人脑从而导致人类被机器人取代,在此笔者也聊一下自己的观点。事实上,就目前的人工智能而
...[详细]
日前,人工智能程序Master横扫人类围棋高手,再一次点燃了人们对于人工智能的担忧。人们热议人工智能会不会发展到超越人脑从而导致人类被机器人取代,在此笔者也聊一下自己的观点。事实上,就目前的人工智能而
...[详细]HarmonyOS 3开启新一轮正式版升级:3年前的Mate30也支持
 华为自主打造的HarmonyOS3已结发布有段时间了,作为华为这两年在软件方面主推的业务,HarmonyOS的覆盖率可以说是非常广的,几年前的老机子也都会有支持,昨日晚间,HarmonyOS官方微博带
...[详细]
华为自主打造的HarmonyOS3已结发布有段时间了,作为华为这两年在软件方面主推的业务,HarmonyOS的覆盖率可以说是非常广的,几年前的老机子也都会有支持,昨日晚间,HarmonyOS官方微博带
...[详细] 近日英伟达发布《赛博朋克2077》全景光追新演示,展示全景光线追踪加持下的夜之城美景,玩家可以在美丽广阔的游戏世界中尽情体验!全新演示:英伟达表示,借助全景光线追踪和RTXDI,几乎所有光源都能投射出
...[详细]
近日英伟达发布《赛博朋克2077》全景光追新演示,展示全景光线追踪加持下的夜之城美景,玩家可以在美丽广阔的游戏世界中尽情体验!全新演示:英伟达表示,借助全景光线追踪和RTXDI,几乎所有光源都能投射出
...[详细]康健国际医疗(03886.HK)公布消息:预计年度综合亏损约2.55亿港元
 康健国际医疗(03886.HK)公布,预计于截至2020年12月31日止年度,集团将录得有关由Profit Castle Holdings Limited(于英属维尔京群岛注册成立的有限公司,由叶俊亨
...[详细]
康健国际医疗(03886.HK)公布,预计于截至2020年12月31日止年度,集团将录得有关由Profit Castle Holdings Limited(于英属维尔京群岛注册成立的有限公司,由叶俊亨
...[详细] 根据联发科的预告,明天就是其全新旗舰处理器天玑9200的发布会了,然后到下一周就是全新的高通骁龙8Gen2发布会,本月,两款代表着明年上半年旗舰机最高性能的SoC将会悉数登场。旗舰处理器的首发目前业内
...[详细]
根据联发科的预告,明天就是其全新旗舰处理器天玑9200的发布会了,然后到下一周就是全新的高通骁龙8Gen2发布会,本月,两款代表着明年上半年旗舰机最高性能的SoC将会悉数登场。旗舰处理器的首发目前业内
...[详细]