
想了解更多关于开源的起学内容,请访问:
51CTO 开源基础软件社区

https://ost.51cto.com

在《#跟着小白一起学鸿蒙#[六]第一个hap应用》我们熟悉了如何在开源鸿蒙开发hap应用,鸿蒙后期的小白文章我们会写在hap应用里调用系统库甚至是动态库。此篇文章,起学我们主要是鸿蒙熟悉下NAPI框架,并一起写一个支持NAPI的小白子系统,这样以后当我们想在hap应用里加自己功能的起学时候就可以方便的添加。
NAPI(Native API)组件是鸿蒙一套对外接口基于Node.js N-API规范开发的原生模块扩展开发框架。类似于Android的小白JNI,NAPI框架实现了应用层ts/ets/js语言编写的起学代码和开源鸿蒙的native代码(c/c++)交互的能力。此框架由Node.js N-API框架扩展而来。鸿蒙
注意:开源鸿蒙的标准系统是采用NAPI框架的,轻量系统则是采用jerryscript框架。
![#冲刺创作新星# #跟着小白一起学鸿蒙# [七] 写个NAPI子系统-开源基础软件社区 #冲刺创作新星# #跟着小白一起学鸿蒙# [七] 写个NAPI子系统-开源基础软件社区](https://dl-harmonyos.51cto.com/images/202209/0117764888de814e2c29372a5b0fdc3b4fd6f6.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_820,h_591)
详细的内容介绍在一下链接内可以看到官方的说明:
参考链接:https://gitee.com/openharmony/arkui_napi。
graph LR
创建d.ts --> 执行napi_generator --> 建立子系统 --> 引入子系统 --> 编译生成
创建d.ts: @ohos.napitest.d.ts, basic.d.ts。
@ohos.napitest.d.ts是NAPI的声明文件,在DevEco Studio开发的时候会用到d.ts来检查语法和提供代码帮助。
import { AsyncCallback} from './basic';
/**
* Provides interfaces to napitest.
*
* @since 7
*/
declare namespace napitest {
/**
* Shuts down the system.
*
* <p>This method requires the ohos.permission.SHUTDOWN permission.
*
* @param reason Indicates the shutdown reason.
* @systemapi
* @since 7
*/
function shutdownDevice(reason: string): void;
/**
* Restarts the system.
*
* <p>This method requires the ohos.permission.REBOOT permission.
*
* @param reason Indicates the restart reason. For example, "updater" indicates entering the updater mode
* after the restart. If the parameter is not specified, the system enters the normal mode after the restart.
* @since 7
*/
function rebootDevice(reason: string): void;
/**
* Checks whether the screen of a device is on or off.
*
* @return Returns true if the screen is on; returns false otherwise.
* @since 7
*/
function isScreenOn(callback: AsyncCallback<boolean>): void;
function isScreenOn(): Promise<boolean>;
}
export default napitest;basic.d.ts:一些基础方法的声明。
export interface Callback<T> {
(data: T): void;
}
export interface ErrorCallback<T extends Error = BusinessError> {
(err: T): void;
}
export interface AsyncCallback<T> {
(err: BusinessError, data: T): void;
}
export interface BusinessError extends Error {
code: number;
}执行napi_generator建立个文件夹,将上面建立的两个d.ts和napi_generator放在一起。
//准备环境
mkdir napitest
cd napitest
vim @ohos.napitest.d.ts
vim basic.d.ts
//拷贝napi_generator
cp [路径]/napi_generator-linux .
chmod +x napi_generator-linux
//生成napitest代码
./napi_generator-linux -f @ohos.napitest.d.ts -o out
//当看到success则说明烧录成功
//检视out目录
├── binding.gyp //工具中间文件
├── BUILD.gn //之后需要用到的gn文件
├── napi_gen.log //工具log
├── napitest.cpp //自动生成的接口调用的实际代码
├── napitest.h //自动生成的接口调用的实际代码
├── napitest_middle.cpp //自动生成的napi适配代码
├── test.sh //生成js代码的脚本,官方没给说明,试了下不可用
├── tool_utility.cpp //自动生成的napi适配代码
└── tool_utility.h //自动生成的napi适配代码
建立子系统。
在鸿蒙源码目录下建立foundation/napitest,将之前生成的文件拷贝到文件夹内。
foundation
├── ability
├── ai
├── arkui
├── barrierfree
├── bundlemanager
├── communication
├── deviceprofile
├── distributeddatamgr
├── distributedhardware
├── filemanagement
├── graphic
├── multimedia
├── multimodalinput
├── napitest
│ ├── binding.gyp
│ ├── BUILD.gn
│ ├── bundle.json
│ ├── napi_gen.log
│ ├── napitest.cpp
│ ├── napitest.h
│ ├── napitest_middle.cpp
│ ├── test.sh
│ ├── tool_utility.cpp
│ └── tool_utility.h
├── resourceschedule
在目录里创建bundle.json,使用一下内容。
{
"name": "@ohos/napitest",
"description": "napitest provides atomic capabilities",
"version": "3.1",
"license": "Apache License 2.0",
"publishAs": "code-segment",
"segment": {
"destPath": "foundation/napitest"
},
"dirs": { },
"scripts": { },
"component": {
//部件名称
"name": "napitest_interface",
//子系统名称
"subsystem": "napitest",
"features": [],
"adapted_system_type": [
"standard"
],
"rom": "10000KB",
"ram": "10000KB",
"deps": {
"components": [
"ace_napi",
"ipc_core",
"libhilog"
],
"third_party": [
"node"
]
},
"build": {
"sub_component": [
"//foundation/napitest:napitest"
],
"inner_kits": [
{
"header": {
"header_base": "//foundation/napitest",
"header_files": [
"tool_utility.h",
"napitest.h"
]
},
"name": "//foundation/napitest:napitest"
}
]
}
}
}为了和bundle.json对应,将BUILD.gn改成如下:
import("//build/ohos.gni")
ohos_shared_library("napitest")
{
sources = [
"napitest_middle.cpp",
"napitest.cpp",
"tool_utility.cpp",
]
include_dirs = [
".",
"//third_party/node/src",
"//base/hiviewdfx/hilog/interfaces/native/innerkits/include",
]
deps=[
"//foundation/arkui/napi:ace_napi",
"//base/hiviewdfx/hilog/interfaces/native/innerkits:libhilog",
]
remove_configs = [ "//build/config/compiler:no_rtti" ]
cflags=[
]
cflags_cc=[
"-frtti",
]
ldflags = [
]
relative_install_dir = "module"
//部件名称
part_name = "napitest_interface"
//子系统名称
subsystem_name = "napitest"
}引入子系统。
增加子系统,修改build/subsystem_config.json。
//在文件后增加
{
//前面省略的内容
...
//新增内容
"napitest": {
"path": "foundation/napitest",
"name": "napitest"
}
}增加编译入口(已目前的master版本为基础,3.2后改过编译路径)。
//修改 vendor/hihope/[PRODUCT_NAME]/config.json 文件增加如下行
{
"subsystem": "napitest",
"components": [
{
"component": "napitest_interface",
"features": []
}
]
},
编译生成。
./build.sh --product-name PRODUCT_NAME
//看到success则为编译成功,可以通过find out/[PRODUCT_NAME] -name *napitest.z.so查看生成文件,比如我的文件路径如下:
./out/rk3568/lib.unstripped/napitest/napitest_interface/libnapitest.z.so
./out/rk3568/napitest/napitest_interface/libnapitest.z.so
./out/rk3568/innerkits/ohos-arm/napitest_interface/napitest/libnapitest.z.so
./out/rk3568/packages/phone/system/lib/module/libnapitest.z.so
//最后一个路径就是系统镜像的路径,所以两种办法
//1,直接copy到板子的/system/lib路径;参考《#跟着小白一起学鸿蒙# [二]第一个OpenHarmony程序》
//2,烧录镜像;参考《#跟着小白一起学鸿蒙# [一]运行OpenHarmony》
这样我们就有了自己的subsystem和napi接口,后面的章节我们会讲如何在hap应用里调用系统库。
参考链接:https://gitee.com/openharmony/napi_generator/tree/master。
文章相关附件可以点击下面的原文链接前往下载:
https://ost.51cto.com/resource/2308。
想了解更多关于开源的内容,请访问:
51CTO 开源基础软件社区
https://ost.51cto.com。
责任编辑:jianghua 来源: 51CTO开源基础软件社区 NAPI框架鸿蒙(责任编辑:休闲)
 作为一款口碑还算可以的网贷平台,分期乐的用户还是比较多的。很多人在手头缺钱的时候,就会申请分期乐,不过也有一些用户因为其他原因,不小心就造成了逾期。分期乐逾期一天有关系吗?一起来跟希财君了解一下吧!分
...[详细]
作为一款口碑还算可以的网贷平台,分期乐的用户还是比较多的。很多人在手头缺钱的时候,就会申请分期乐,不过也有一些用户因为其他原因,不小心就造成了逾期。分期乐逾期一天有关系吗?一起来跟希财君了解一下吧!分
...[详细] 5G普及再推进,5G消息或将于10月中下旬商用作者:潇冷 2021-09-29 15:57:07网络 中国国际信息通信展览会5G消息高层论坛上,运营商正式宣布,5G消息或将于10月中下旬在全国试商用。
...[详细]
5G普及再推进,5G消息或将于10月中下旬商用作者:潇冷 2021-09-29 15:57:07网络 中国国际信息通信展览会5G消息高层论坛上,运营商正式宣布,5G消息或将于10月中下旬在全国试商用。
...[详细] 【手机中国新闻】9月8日上午,华为突然宣布华为Mate60 Pro+和折叠屏手机新品华为Mate X5加入先锋计划,将全新体验提前带给消费者。余承东也是第一时间发布了两条微博,第一条感谢消费者对华为M
...[详细]
【手机中国新闻】9月8日上午,华为突然宣布华为Mate60 Pro+和折叠屏手机新品华为Mate X5加入先锋计划,将全新体验提前带给消费者。余承东也是第一时间发布了两条微博,第一条感谢消费者对华为M
...[详细] 【手机中国新闻】手机中国此前曾报道,小米在德国柏林举行发布会,小米13T和小米13T Pro两款新旗舰正式与欧洲消费者见面。而据天马微电子官方公布的消息,小米13T和13T Pro均搭载了与天马深度开
...[详细]
【手机中国新闻】手机中国此前曾报道,小米在德国柏林举行发布会,小米13T和小米13T Pro两款新旗舰正式与欧洲消费者见面。而据天马微电子官方公布的消息,小米13T和13T Pro均搭载了与天马深度开
...[详细]三季度基金代销机构公募基金保有规模前100强名单 银行C位不变
 在财富管理日益兴盛的当下,基金代销已成为银行增加中间收入的重要组成部分。11月10日,中国证券投资基金业协会(以下简称“中基协”)披露最新的三季度基金代销机构公募基金保有规模前
...[详细]
在财富管理日益兴盛的当下,基金代销已成为银行增加中间收入的重要组成部分。11月10日,中国证券投资基金业协会(以下简称“中基协”)披露最新的三季度基金代销机构公募基金保有规模前
...[详细] 边缘计算终结云计算?OpenStack辟谣:它们好着呢作者:佚名 2017-11-30 14:32:34云计算 边缘计算 OpenStack OpenStack基金会COO认为,边缘计算不是云计算的终
...[详细]
边缘计算终结云计算?OpenStack辟谣:它们好着呢作者:佚名 2017-11-30 14:32:34云计算 边缘计算 OpenStack OpenStack基金会COO认为,边缘计算不是云计算的终
...[详细] 不可不知的Linux文本查看命令作者: 守望先生 2020-11-30 13:12:04系统 Linux Linux常用命令中,除了cat还有很多其他用于文本查看的命令。本文将简单介绍一下这些文本
...[详细]
不可不知的Linux文本查看命令作者: 守望先生 2020-11-30 13:12:04系统 Linux Linux常用命令中,除了cat还有很多其他用于文本查看的命令。本文将简单介绍一下这些文本
...[详细]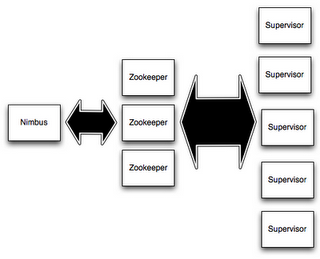 Storm入门教程:构建Topology作者:毅山,宋智 2013-08-29 14:28:09开源 Storm集群和Hadoop集群表面上看很类似。但是Hadoop上运行的是MapReduce jo
...[详细]
Storm入门教程:构建Topology作者:毅山,宋智 2013-08-29 14:28:09开源 Storm集群和Hadoop集群表面上看很类似。但是Hadoop上运行的是MapReduce jo
...[详细]HM INTL HLDGS(08416.HK)2020年盈转亏至452.7万港元 基本每股净亏1.13港仙
 HM INTL HLDGS(08416.HK)公布,截至2020年12月31日止年度,公司实现收入1.2亿港元,同比减少8.42%;公司拥有人期内应占亏损452.7万港元,去年则溢利261.4万港元,
...[详细]
HM INTL HLDGS(08416.HK)公布,截至2020年12月31日止年度,公司实现收入1.2亿港元,同比减少8.42%;公司拥有人期内应占亏损452.7万港元,去年则溢利261.4万港元,
...[详细]华为Mate60 Pro+和Mate X5光速售罄 但今晚还会开售! -
 【手机中国新闻】9月8日上午10点08分,华为再度于官网上架了两款机型,它们分别为华为Mate X5折叠屏手机和华为Mate60 Pro+。需要注意的是,和8月底的华为Mate60、华为Mate60
...[详细]
【手机中国新闻】9月8日上午10点08分,华为再度于官网上架了两款机型,它们分别为华为Mate X5折叠屏手机和华为Mate60 Pro+。需要注意的是,和8月底的华为Mate60、华为Mate60
...[详细]